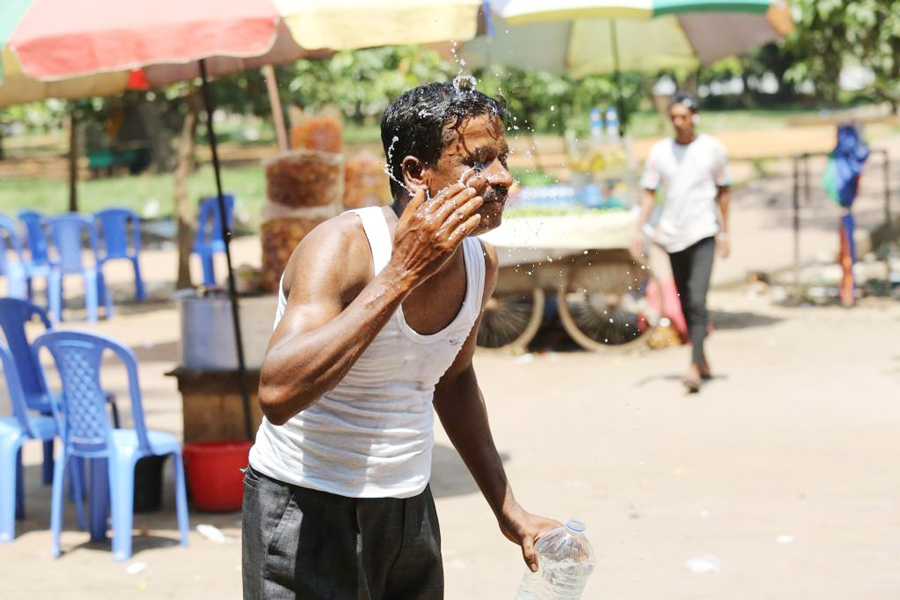
Published :
Updated :
Excessive heatwaves in Bangladesh have emerged as a significant threat to the country's economy, impacting various sectors and exacerbating socio-economic vulnerabilities. As temperatures rise and heatwaves become more frequent and severe, the economic repercussions are profound, affecting agriculture, industry, health, infrastructure, and overall productivity.
The agricultural sector, which employs a substantial portion of the population in Bangladesh, bears the brunt of heatwave-induced damages. Prolonged periods of extreme heat lead to water stress, reduced soil moisture, and heat-related stress on crops.
Staple crops such as rice, wheat, and jute are particularly vulnerable, with heatwaves disrupting planting schedules, affecting yields, and increasing pest infestations. The economic losses incurred by farmers due to crop failures, reduced productivity, and increased input costs during heat waves contribute to food insecurity and rural livelihood challenges.
Livestock farming also faces significant economic strains during heatwaves. Heat stress in animals reduces milk production, weight loss, and increased mortality rates. Farmers incur losses in terms of lower marketable yields, decreased quality of animal products, and heightened healthcare expenses for livestock management. The cumulative impact on the livestock sector increases the economic burden on rural communities and agricultural stakeholders.
The industrial and manufacturing sectors experience disruptions and productivity losses during heatwaves. High temperatures can lead to equipment failures, reduced efficiency in production processes, and increased energy consumption for cooling and ventilation. Industries reliant on outdoor labour, such as construction, face challenges in worker safety, reduced productivity, and project delays. The economic costs associated with downtime, repairs, and operational inefficiencies during heatwaves contribute to financial strain for businesses and hinder economic growth.
The energy sector grapples with heightened demand for cooling services during heatwaves, leading to power shortages, load shedding, and strain on electricity grids. Increased usage of air conditioning units and cooling appliances exacerbates energy consumption and carbon emissions, further amplifying the environmental footprint of heatwave impacts. The economic implications include higher electricity bills for consumers, increased operational costs for utilities, and challenges in meeting peak demand without compromising grid stability.
The tourism and hospitality industry, a significant contributor to Bangladesh's economy, faces challenges during heatwaves. High temperatures deter domestic and international tourists, impacting hotel occupancy rates, tourism revenues, and related businesses such as restaurants, transportation, and recreational activities. Heat-related discomfort and health concerns among tourists further dampen the tourism sector's economic prospects during peak heatwave periods.
Healthcare expenditures escalate during heatwaves due to increased heat-related illnesses, hospital admissions, and emergency healthcare services. The economic burden on the healthcare sector includes costs associated with treatment, medical supplies, capacity expansion to cope with patient influx, and public health campaigns to raise awareness about heat-related risks. The strain on healthcare infrastructure and resources during heatwaves highlights the need for adaptive measures and investment in climate-resilient healthcare systems.
Infrastructure vulnerabilities are exacerbated by heatwaves, leading to economic losses in terms of damage to roads, bridges, buildings, and utilities. Heat-induced stresses on infrastructure materials, such as asphalt roads and concrete structures, contribute to deterioration, maintenance challenges, and increased repair costs. The economic impact extends to transportation disruptions, supply chain interruptions, and reduced operational efficiency across sectors reliant on robust infrastructure networks.
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs), a vital engine of economic growth and employment generation, face unique challenges during heat waves. SMEs operating in sectors sensitive to climate conditions, such as agriculture, textiles, and food processing, experience disruptions in production, supply chain constraints, and market uncertainties. The economic strain on SMEs includes revenue losses, liquidity challenges, and difficulties accessing financing and insurance to cope with heatwave-related risks.
To address the economic challenges posed by excessive heatwaves in Bangladesh, a multi-faceted approach is essential, encompassing climate adaptation, resilience-building measures, policy interventions, and stakeholder collaboration.
Investments in climate-resilient agriculture are paramount to enhancing agricultural productivity and reducing vulnerability to heatwave impacts. This includes promoting drought-resistant crop varieties, efficient irrigation systems, soil moisture conservation techniques, and early warning systems for weather-related risks. Financial incentives, credit facilities, and insurance schemes tailored to agricultural resilience can support farmers in adopting climate-smart practices and mitigating economic losses during heat waves.
Promoting renewable energy sources and efficiency measures can alleviate pressure on the energy sector during heatwaves. Investments in solar power, wind energy, and other renewable technologies diversify the energy mix, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance energy security. Energy conservation initiatives, demand-side management programs, and public awareness campaigns on sustainable energy practices contribute to economic savings, resilience, and environmental sustainability.
Climate-resilient infrastructure development is critical for mitigating heatwave impacts on transportation, utilities, and urban areas. This includes incorporating heat-resistant materials, green infrastructure, urban cooling strategies, and climate-responsive design standards in infrastructure projects. Improved drainage systems, flood protection measures, and resilient building codes enhance infrastructure resilience to extreme weather events, including heatwaves, reducing economic losses and improving community well-being.
Public health interventions are crucial in reducing healthcare costs and mitigating heat-related health risks. Heat-health action plans, early warning systems, heatwave preparedness training for healthcare professionals, and community outreach programs raise awareness about heat-related illnesses and promote adaptive behaviours. Accessible healthcare services, cooling centers, and emergency response mechanisms ensure timely interventions and reduce the economic burden of heatwave-induced healthcare demands.
Capacity-building and knowledge-sharing initiatives empower communities, businesses, and policymakers to address heatwave challenges effectively. Training programmes on climate resilience, disaster risk management, heat stress mitigation, and business continuity planning equip stakeholders with skills and resources to adapt to heatwave impacts. Knowledge exchange platforms, research partnerships, and best practice sharing facilitate learning and innovation in heatwave resilience strategies.
Policy frameworks must integrate heatwave resilience into national development agendas, sectoral plans, and regulatory frameworks. This includes mainstreaming climate adaptation, disaster risk reduction, and heatwave management considerations across policy domains. Incentives for climate-smart investments, regulatory incentives for energy efficiency, and fiscal measures to support vulnerable sectors enhance economic resilience to heatwaves and promote sustainable development.
International cooperation and partnerships are instrumental in addressing transboundary challenges posed by heat waves and climate change. Collaborative initiatives on technology transfer, capacity building, finance mobilisation, and knowledge exchange strengthen resilience efforts and foster global solidarity. Engagement with international organisations, donor agencies, research institutions, and private sector partners leverages resources and expertise to support Bangladesh's efforts in building a climate-resilient economy.
The economic toll of excessive heatwaves in Bangladesh underscores the urgent need for comprehensive and proactive strategies to build resilience, mitigate risks, and promote sustainable development. By investing in climate adaptation, renewable energy, resilient infrastructure, public health, and stakeholder engagement, Bangladesh can navigate the challenges posed by heat waves and build a more resilient and prosperous future for its economy and society.
Dr Matiur Rahman is researcher and development worker. matiurrahman588@gmail.com


 For all latest news, follow The Financial Express Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Financial Express Google News channel.